人工智能/机器学习基础知识——激活函数汇总
人工智能/机器学习基础知识——激活函数汇总
激活函数
Activation Function
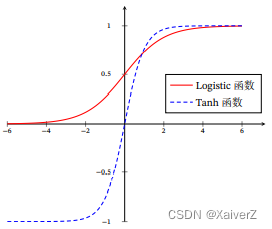
Sigmoid(Logistic)
Sigmoid(Logistic)
-
数学描述
σ ( x ) = 1 1 + exp ( − x ) \sigma(x)=\frac{1}{1+\exp (-x)} σ(x)=1+exp(−x)1
-
由于Sigmoid函数的特性,一些不适当的参数初始化会造成神经元过饱和(Fully Saturated),使Sigmoid的函数值过于趋近两端,造成梯度消失
Tanh
Tanh
-
数学描述
tanh ( x ) = exp ( x ) − exp ( − x ) exp ( x ) + exp ( − x ) \tanh (x)=\frac{\exp (x)-\exp (-x)}{\exp (x)+\exp (-x)} tanh(x)=exp(x)+exp(−x)exp(x)−exp(−x)
-
由于Tanh函数的特性,一些不适当的参数初始化会造成神经元过饱和(Fully Saturated),使Tanh的函数值过于趋近两端,造成梯度消失
-
Tanh函数的输出是零中心化的(Zero-Centered),而Logistic函数的输出恒大于 0.非零中心化的输出会使得其后一层的神经元的输入发生偏置偏移(Bias Shift),并进一步使得梯度下降的收敛速度变慢

Hard-Logistic & Hard-Tanh
Hard-Logistic & Hard-Tanh
-
基于泰勒展开逼近原函数值
hard-logistic ( x ) = { 1 g l ( x ) ≥ 1 g l 0 < g l ( x ) < 1 0 g l ( x ) ≤ 0 = max ( min ( g l ( x ) , 1 ) , 0 ) = max ( min ( 0.25 x + 0.5 , 1 ) , 0 ) . \begin{aligned} \text { hard-logistic }(x) &= \begin{cases}1 & g_{l}(x) \geq 1 \\ g_{l} & 0<g_{l}(x)<1 \\ 0 & g_{l}(x) \leq 0\end{cases} \\ &=\max \left(\min \left(g_{l}(x), 1\right), 0\right) \\ &=\max (\min (0.25 x+0.5,1), 0) . \end{aligned} hard-logistic (x)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧1gl0gl(x)≥10<gl(x)<1gl(x)≤0=max(min(gl(x),1),0)=max(min(0.25x+0.5,1),0).
hard-tanh ( x ) = max ( min ( g t ( x ) , 1 ) , − 1 ) = max ( min ( x , 1 ) , − 1 ) \begin{aligned} \text { hard-tanh }(x) &=\max \left(\min \left(g_{t}(x), 1\right),-1\right) \\ &=\max (\min (x, 1),-1) \end{aligned} hard-tanh (x)=max(min(gt(x),1),−1)=max(min(x,1),−1)

ReLU
Rectified Linear Unit
-
数学描述
ReLU ( x ) = { x x ≥ 0 0 x < 0 = max ( 0 , x ) . \begin{aligned} \operatorname{ReLU}(x) &= \begin{cases}x & x \geq 0 \\ 0 & x<0\end{cases} \\ &=\max (0, x) . \end{aligned} ReLU(x)={x0x≥0x<0=max(0,x).
-
死亡ReLU问题
Dying ReLU Problem
- 如果参数在一次不恰当的更新后,第一个隐藏层中的某个ReLU神经元在所有的训练数据上都不能被激活,那么这个神经元自身参数的梯度永远都会是0,在以后的训练过程中永远不能被激活,并且也有可能会发生在其他隐藏层
Leaky ReLU
Leaky ReLU
-
数学描述
LeakyReLU ( x ) = { x if x > 0 γ x if x ≤ 0 = max ( 0 , x ) + γ min ( 0 , x ) \begin{aligned} \operatorname{LeakyReLU}(x) &= \begin{cases}x & \text { if } x>0 \\ \gamma x & \text { if } x \leq 0\end{cases} \\ &=\max (0, x)+\gamma \min (0, x) \end{aligned} LeakyReLU(x)={xγx if x>0 if x≤0=max(0,x)+γmin(0,x)
PReLU
Parametric ReLU
-
数学描述
PReLU i ( x ) = { x if x > 0 γ i x if x ≤ 0 = max ( 0 , x ) + γ i min ( 0 , x ) \begin{aligned} \operatorname{PReLU}_{i}(x) &= \begin{cases}x & \text { if } x>0 \\ \gamma_{i} x & \text { if } x \leq 0\end{cases} \\ &=\max (0, x)+\gamma_{i} \min (0, x) \end{aligned} PReLUi(x)={xγix if x>0 if x≤0=max(0,x)+γimin(0,x)
ELU
Exponential Linear Unit
-
数学描述
ELU ( x ) = { x if x > 0 γ ( exp ( x ) − 1 ) if x ≤ 0 = max ( 0 , x ) + min ( 0 , γ ( exp ( x ) − 1 ) ) \begin{aligned} \operatorname{ELU}(x) &= \begin{cases}x & \text { if } x>0 \\ \gamma(\exp (x)-1) & \text { if } x \leq 0\end{cases} \\ &=\max (0, x)+\min (0, \gamma(\exp (x)-1)) \end{aligned} ELU(x)={xγ(exp(x)−1) if x>0 if x≤0=max(0,x)+min(0,γ(exp(x)−1))
SELU
Scaled Exponential Linear Unit
-
数学描述
SELU ( x ) = scale ∗ ( max ( 0 , x ) + min ( 0 , α ∗ ( exp ( x ) − 1 ) ) ) = scale ∗ ELU ( x , α ) \text{SELU}(x) = \text{scale} * (\max(0,x) + \min(0, \alpha * (\exp(x) - 1))) = \text{scale} * \text{ELU}(x, \alpha) SELU(x)=scale∗(max(0,x)+min(0,α∗(exp(x)−1)))=scale∗ELU(x,α)
其中, scale \text{scale} scale与 α \alpha α为超参数α = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717 \alpha = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717 α=1.6732632423543772848170429916717
scale = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946 \text{scale} = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946 scale=1.0507009873554804934193349852946
Softplus
Softplus
-
数学描述
Softplus ( x ) = log ( 1 + exp ( x ) ) \text { Softplus }(x)=\log (1+\exp (x)) Softplus (x)=log(1+exp(x))

Swish
Swish
-
数学描述
swish ( x ) = x σ ( β x ) \operatorname{swish}(x)=x \sigma(\beta x) swish(x)=xσ(βx)

GELU
Gaussian Error Linear Unit
-
数学描述
GELU ( x ) = x P ( X ≤ x ) \operatorname{GELU}(x)=x P(X \leq x) GELU(x)=xP(X≤x)
Maxout
Maxout
-
数学描述
z k = w k ⊤ x + b k z_{k}=\boldsymbol{w}_{k}^{\top} \boldsymbol{x}+b_{k} zk=wk⊤x+bk
maxout ( x ) = max k ∈ [ 1 , K ] ( z k ) \operatorname{maxout}(\boldsymbol{x})=\max _{k \in[1, K]}\left(z_{k}\right) maxout(x)=k∈[1,K]max(zk)
GLU
Gated Linear Unit
-
数学描述
h l ( X ) = ( X ∗ W + b ) ⊗ σ ( X ∗ V + c ) h_{l}(\mathbf{X})=(\mathbf{X} * \mathbf{W}+\mathbf{b}) \otimes \sigma(\mathbf{X} * \mathbf{V}+\mathbf{c}) hl(X)=(X∗W+b)⊗σ(X∗V+c)
其中, W , V , b , c \mathbf{W}, \mathbf{V}, \mathbf{b}, \mathbf{c} W,V,b,c为可学习参数, σ ( ⋅ ) \sigma(·) σ(⋅)为Sigmoid
GTU
Gated Tanh Unit
-
数学描述
h l ( X ) = tanh ( X ∗ W + b ) ⊗ σ ( X ∗ V + c ) h_{l}(\mathbf{X})=\tanh (\mathbf{X} * \mathbf{W}+\mathbf{b}) \otimes \sigma(\mathbf{X} * \mathbf{V}+\mathbf{c}) hl(X)=tanh(X∗W+b)⊗σ(X∗V+c)
其中, W , V , b , c \mathbf{W}, \mathbf{V}, \mathbf{b}, \mathbf{c} W,V,b,c为可学习参数, σ ( ⋅ ) \sigma(·) σ(⋅)为Sigmoid, t a n h ( ⋅ ) tanh(·) tanh(⋅)为Tanh
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)